[Student] Prerequisite skills/knowledge
Students should be moderately comfortable in a Fab Lab environment and be capable of some amount of self-guided work. They should have some experience with the following software, processes and equipment:
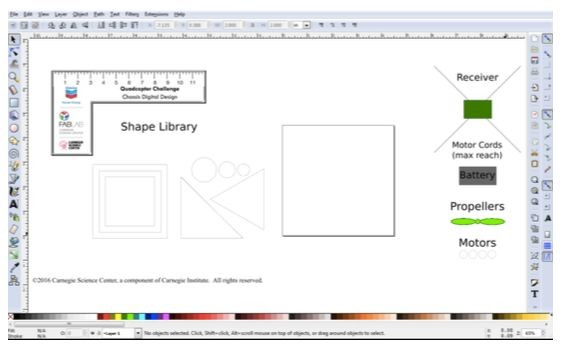
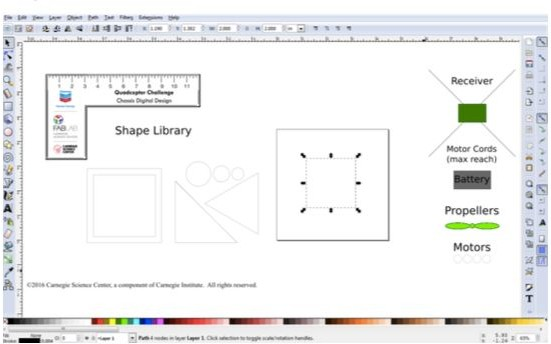
- Inkscape (or equivalent 2D vector graphics software)
- Laser cutting (or similar subtractive CNC machine)
- Basic soldering
Key Vocabulary:
- Accelerometer – A sensor that measures the tilting motion of the
- Bernoulli’s principle – The principle that an increase in the velocity of a stream of fluid results in a decrease in pressure. Therefore, on a curved wing, the air pressure on top of the wing is lower than below, creating a vacuum that “sucks” the wing upward.
- CAD – Computer aided design
- CAM – Computer aided manufacturing
- Center of gravity – A point from which the weight of a body or system may be considered to act.
- CNC – Computer numerical
- Drone – A remote-controlled or autonomous pilotless aircraft .
- Electromagnet – A magnet whose magnetic field is produced by an electric current, consisting of a wire wrapped around a metal When electricity is run through the wire, the electromagnet is turned on.
- Engineering – Using technological and scientific knowledge to solve practical problems.
- Gyro sensor – Devices that sense angular In simple terms, angular velocity is the change in rotational angle per unit of time. This particular quadcopter uses a tiny vibrational gyro, embedded in the receiver, which features a crystal that can sense change in angular velocity.
- Iterate – Changing and improving a design based upon multiple test
- Prototype – A model built to test a concept. It is not intended to serve as the final product.
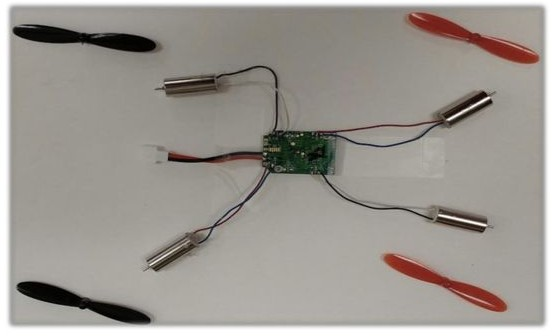
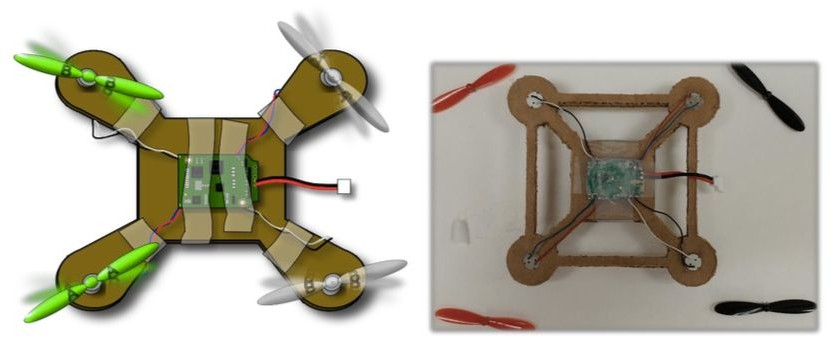
- Quadcopter – An unmanned helicopter having four rotors.
- Robot – A machine that performs complicated tasks and is guided by automatic controls.
- Rotor – A wing that rotates in a circular movement to generate lift.
- Symmetry – Being made up of exactly similar parts facing each other or around an axis.
- Torque – A twisting force.
- UAS – Unmanned aircraft system
Hardware / Software
- Design Computers (one per student is preferred)
- Inkscape CAD software (or equivalent 2D vector graphics design software) https://inkscape.org/en/download/
- Laser cutter
- Soldering irons
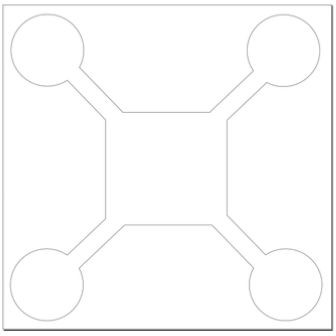
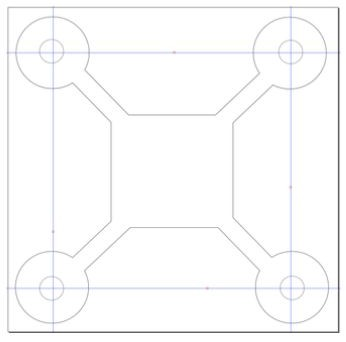
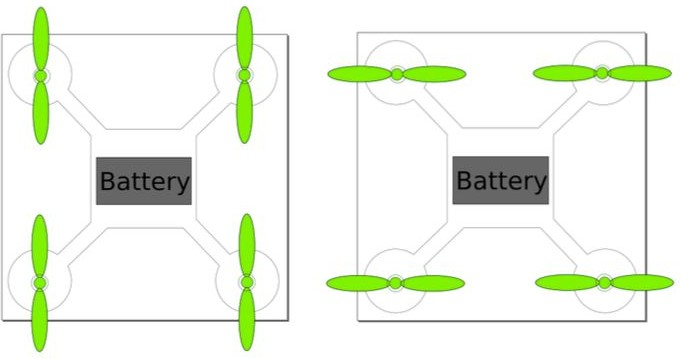
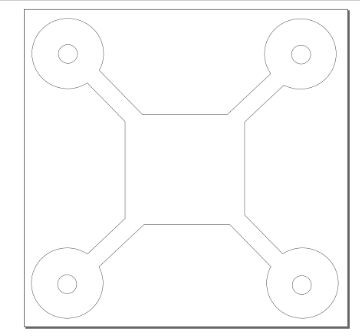
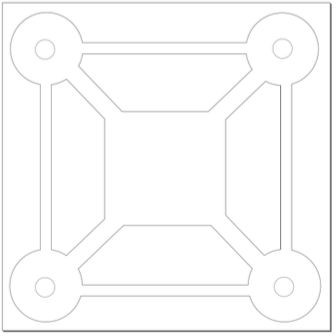
Design Files attachment: QCC Chassis Template.svg
Materials List
General Supply Checklist
- Corrugated plastic sheets
- Corrugated cardboard sheets
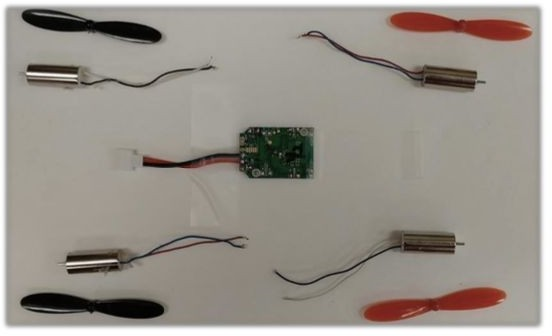
- Quadcopter receivers (Hubsan H107)
- Quadcopter motors (Hubsan H107)
- Lithium-Polymer rechargeable batteries (3.7V / 380 mAh) (Hubsan H107)
- Charging stations (single chargers are best)
- Remote controllers (Hubsan H107)
- Extra AAA batteries
- Extra propellers
- Hot glue
- Scotch tape
- Soldering iron
- Sharpies
- Solder
- Broken quadcopter receivers and motors/old Christmas lights/ LEDs (optional)
- Notebooks (optional, but highly recommended)
Quadcopter Project Materials List
Note: These materials can be purchased directly from Hubsan, at https://www.hubsan.com/. However, their stock tends to be low. It is faster and cheaper to source and purchase parts through domestic importers, found on Amazon. Day-to-day stock and direct links continually change. As long as parts are purchased for the H107L model, they should work without issue. When purchasing, keep in mind that Hubsan sells many different models of quadcopters and drones, so make sure to purchase parts for the H107L.
Shared Materials
- Hubsan H107 4-channel 2.4 GHz radio transmitter
- It is recommended to buy three or more transmitters.
- https://shop.hubsan.com/index.php?main_page=product_info&products_id=434
- Hubsan 3.7V USB charger
- Purchase multiple chargers.
- https://shop.hubsan.com/index.php?main_page=product_info&products_id=432
- Hubsan U-wrench
- Use to remove propellers.
- https://shop.hubsan.com/index.php?main_page=product_info&products_id=435
Per Quadcopter
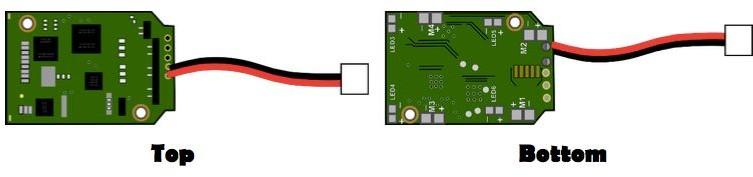
- Hubsan H107 radio receiver and flight controller
- Hubsan H107L motor kit
- Each quadcopter will have two clockwise and two counterclockwise motors.
- Plan to purchase more motors than necessary, to account for inevitable damage and loss.
- https://shop.hubsan.com/index.php?main_page=product_info&products_id=429
- Hubsan H107 propellers
- Each quadcopter will have two clockwise and two counterclockwise propellers.
- Plan to purchase more propellers than necessary, to account for inevitable damage and loss.
- https://shop.hubsan.com/index.php?main_page=product_info&products_id=428
- Hubsan H107 3.7V 380mAh Li-Po Battery
- Each quadcopter can be equipped with a battery.
- It is a good idea to have more batteries than necessary, in order to reduce downtime between flights.
- https://shop.hubsan.com/index.php?main_page=product_info&products_id=431
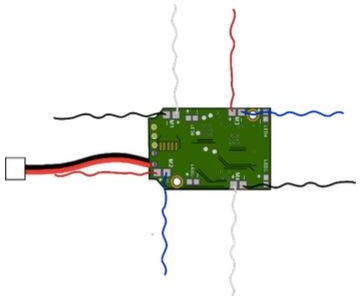
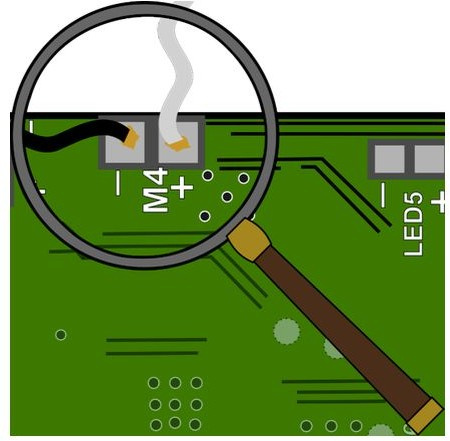
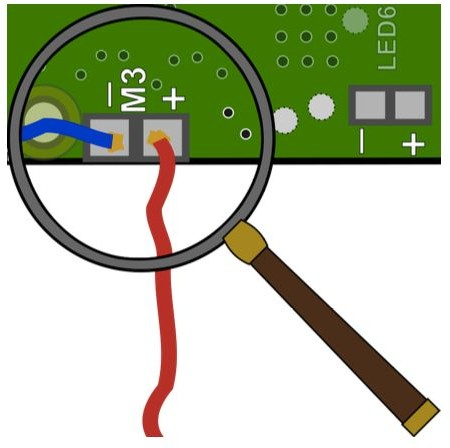
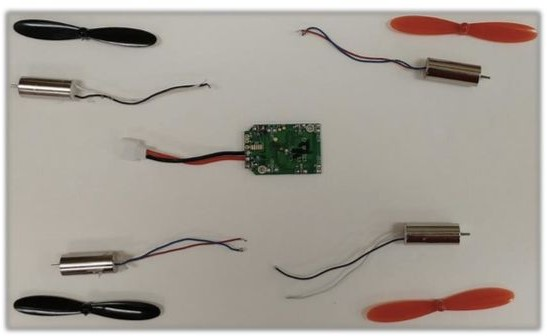
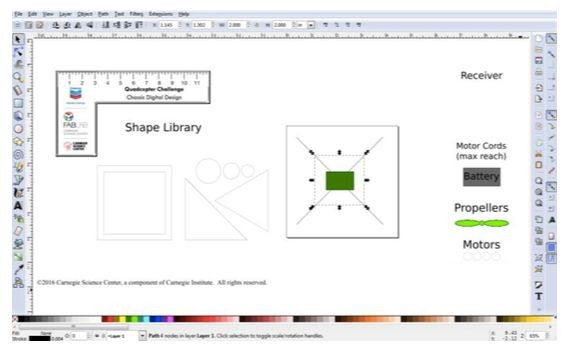
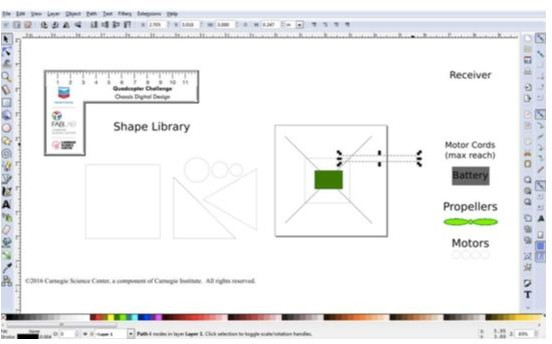
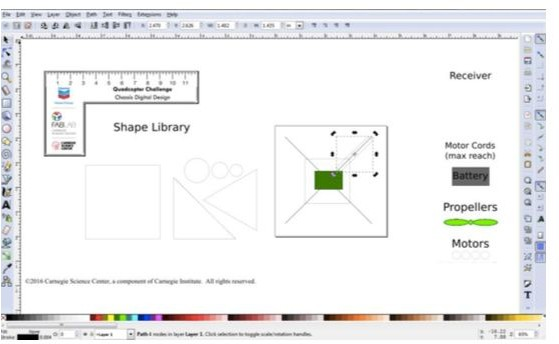
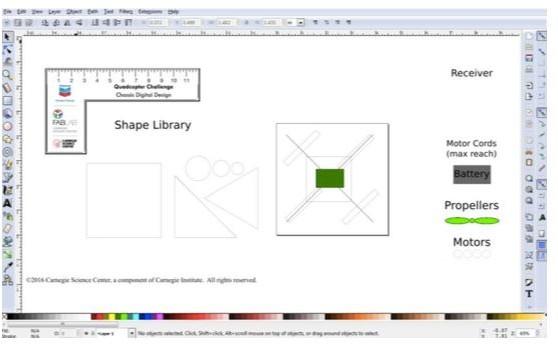
Thank you for your fab contribution!